34 PART II A Deeper Look into a Light Microscope
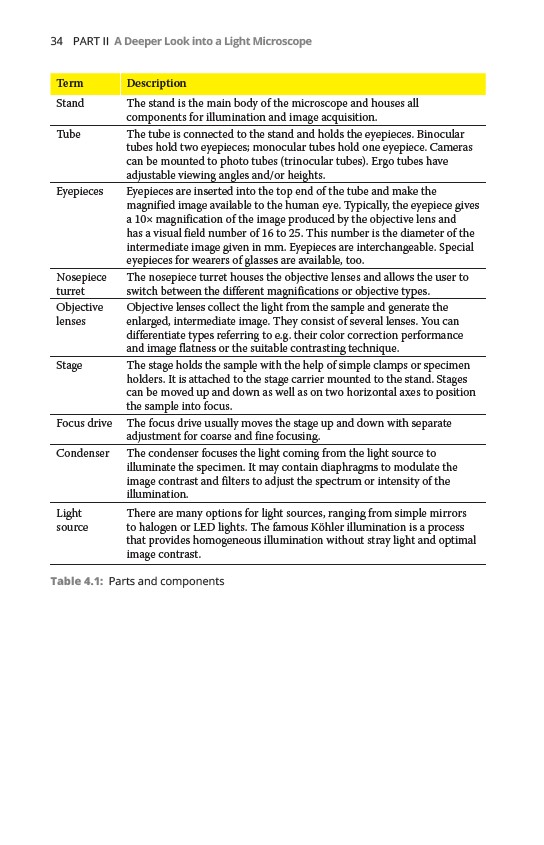
Term Description
Stand The stand is the main body of the microscope and houses all
components for illumination and image acquisition.
Tube The tube is connected to the stand and holds the eyepieces. Binocular
tubes hold two eyepieces; monocular tubes hold one eyepiece. Cameras
can be mounted to photo tubes (trinocular tubes). Ergo tubes have
adjustable viewing angles and/or heights.
Eyepieces Eyepieces are inserted into the top end of the tube and make the
magnified image available to the human eye. Typically, the eyepiece gives
a 10× magnification of the image produced by the objective lens and
has a visual field number of 16 to 25. This number is the diameter of the
intermediate image given in mm. Eyepieces are interchangeable. Special
eyepieces for wearers of glasses are available, too.
Nosepiece
turret
The nosepiece turret houses the objective lenses and allows the user to
switch between the different magnifications or objective types.
Objective
lenses
Objective lenses collect the light from the sample and generate the
enlarged, intermediate image. They consist of several lenses. You can
differentiate types referring to e.g. their color correction performance
and image flatness or the suitable contrasting technique.
Stage The stage holds the sample with the help of simple clamps or specimen
holders. It is attached to the stage carrier mounted to the stand. Stages
can be moved up and down as well as on two horizontal axes to position
the sample into focus.
Focus drive The focus drive usually moves the stage up and down with separate
adjustment for coarse and fine focusing.
Condenser The condenser focuses the light coming from the light source to
illuminate the specimen. It may contain diaphragms to modulate the
image contrast and filters to adjust the spectrum or intensity of the
illumination.
Light
source
There are many options for light sources, ranging from simple mirrors
to halogen or LED lights. The famous Köhler illumination is a process
that provides homogeneous illumination without stray light and optimal
image contrast.
Table 4.1: Parts and components