74 PART IV Digital Documentation
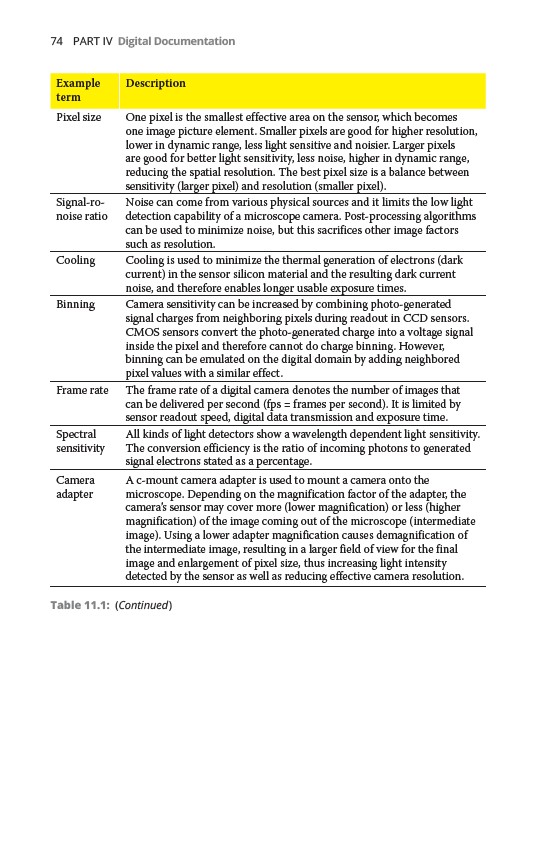
Example
term
Description
Pixel size One pixel is the smallest effective area on the sensor, which becomes
one image picture element. Smaller pixels are good for higher resolution,
lower in dynamic range, less light sensitive and noisier. Larger pixels
are good for better light sensitivity, less noise, higher in dynamic range,
reducing the spatial resolution. The best pixel size is a balance between
sensitivity (larger pixel) and resolution (smaller pixel).
Signal-ronoise
ratio
Noise can come from various physical sources and it limits the low light
detection capability of a microscope camera. Post-processing algorithms
can be used to minimize noise, but this sacrifices other image factors
such as resolution.
Cooling Cooling is used to minimize the thermal generation of electrons (dark
current) in the sensor silicon material and the resulting dark current
noise, and therefore enables longer usable exposure times.
Binning Camera sensitivity can be increased by combining photo-generated
signal charges from neighboring pixels during readout in CCD sensors.
CMOS sensors convert the photo-generated charge into a voltage signal
inside the pixel and therefore cannot do charge binning. However,
binning can be emulated on the digital domain by adding neighbored
pixel values with a similar effect.
Frame rate The frame rate of a digital camera denotes the number of images that
can be delivered per second (fps = frames per second). It is limited by
sensor readout speed, digital data transmission and exposure time.
Spectral
sensitivity
All kinds of light detectors show a wavelength dependent light sensitivity.
The conversion efficiency is the ratio of incoming photons to generated
signal electrons stated as a percentage.
Camera
adapter
A c-mount camera adapter is used to mount a camera onto the
microscope. Depending on the magnification factor of the adapter, the
camera’s sensor may cover more (lower magnification) or less (higher
magnification) of the image coming out of the microscope (intermediate
image). Using a lower adapter magnification causes demagnification of
the intermediate image, resulting in a larger field of view for the final
image and enlargement of pixel size, thus increasing light intensity
detected by the sensor as well as reducing effective camera resolution.
Table 11.1: (Continued)