CHAPTER 6 Well Integrated: HCM in the Hospital IT Landscape 63
As different as the subsystems and modalities are, so are their interfaces. A good
HCM system supports the widest possible range of interfaces. A hospital that
wants to introduce an HCM system should nevertheless try to keep the number of
different interfaces as small as possible. This is because, for maintaining each type
of interface, specialized expertise is necessary. In order to properly channel the flow
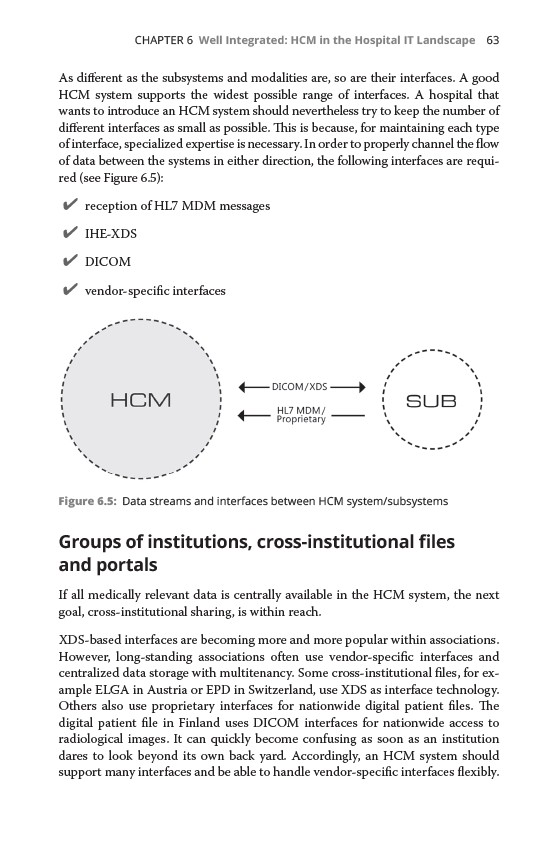
of data between the systems in either direction, the following interfaces are required
(see Figure 6.5):
✔✔ reception of HL7 MDM messages
✔✔ IHE-XDS
✔✔DICOM
✔✔ vendor-specific interfaces
Figure 6.5: Data streams and interfaces between HCM system/subsystems
Groups of institutions, cross-institutional files
and portals
If all medically relevant data is centrally available in the HCM system, the next
goal, cross-institutional sharing, is within reach.
XDS-based interfaces are becoming more and more popular within associations.
However, long-standing associations often use vendor-specific interfaces and
centralized data storage with multitenancy. Some cross-institutional files, for example
ELGA in Austria or EPD in Switzerland, use XDS as interface technology.
Others also use proprietary interfaces for nationwide digital patient files. The
digital
patient file in Finland uses DICOM interfaces for nationwide access to
radiological
images. It can quickly become confusing as soon as an institution
dares to look beyond its own back yard. Accordingly, an HCM system should
support
many interfaces and be able to handle vendor-specific interfaces flexibly.